Time for coffee and tea
Health benefits of black tea: antioxidants found in black tea
Physiology
Recommended Pages
Black Tea Antioxidants
There is much talk about the health properties of green tea but what are the health benefits of black tea? Tea comes from the plant Camellia sinensis, with the best tea coming from the freshest tips of the plant.
Black tea is enjoyed by many people throughout the world and is especially popular in the countries that it is grown in and ones such as the United Kingdom and Turkey; in these last countries tea is most commonly consumed in its black form. It has long been considered a tasty and refreshing drink and thought to have many health benefits.

Black tea leaves such as those shown above are very high in antioxidants such as flavonols and catechins. Photograph by A Girl With Tea.
It is estimated that 80% of all dried tea consumption is in the form of black tea. But what are the compounds in tea that make it healthy? and why do they have antioxidant properties?
Types of Tea
There are three main types of tea all of which come from Camellia sinensis; they are different depending upon their processing methods.
1. Green Tea is made by dehydration of leaves without polyphenol oxidation - This leads to high levels of monomeric polyphenols from catechins.
2. Black tea is produced by fermentation of tea leaves; leading to oxidation and production of multimeric polyphenols.
3. Oolong tea - this is a partially oxidised form of tea.
What is in Black Tea Leaves
Much research has been done on black tea and much is known about the constitution of the leaves. The main constituents of black tea are polyphenolic compounds (36%) carbohydrates (25%), and proteins (15%). There are also significant proportions of lignins, ash and amino acids. Lipids, organic acids, chlorophyll are present. Volatile substances and carotenoids make up less than 0.1% of the dry mass of tea leaves.
Polyphenolic Compounds in Tea
As seen above the biggest group of constituents in black tea are the polyphenolic compounds, of which Flavonols and Catechins are the most abundant form. These compounds contribute to the health benefits of black tea. The amount of flavonols in black tea leaves is dependent upon the age, and they are more common in black teas than in green teas. Some of the catechins in black tea include epigallocatechin, epigallocatechin gallate, epicatechin and epicatechin gallate.
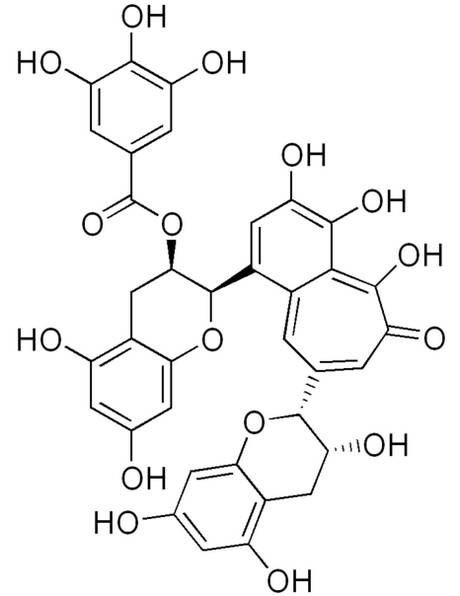
Theaflavin-3-gallate is one of the many antioxidants that are found in black tea. Image reference source.
Luczaj et al (2005). Antioxidant properties of black tea. Prev. Med. 40: 910 to 918
Harold et al. (1992) Green tea composition, consumption and polyphenol chemistry. Prev Med 21:334– 50.